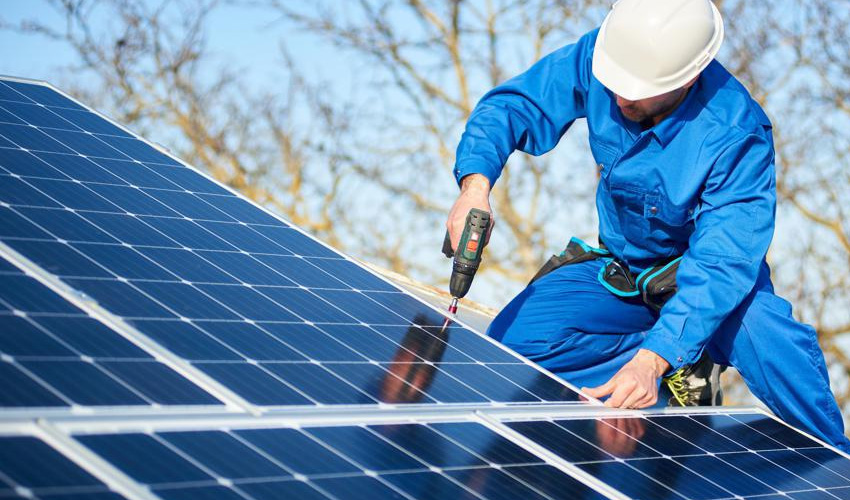
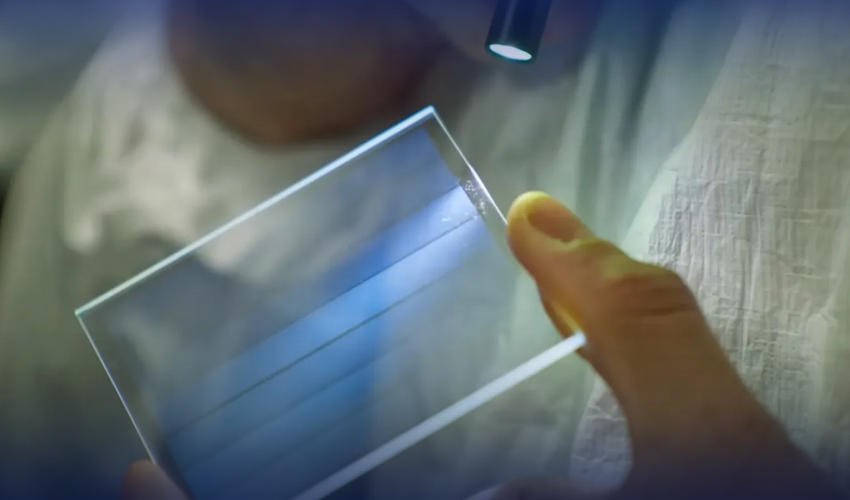
Microsoft's Project Silica has been making waves. This innovative concept aims to transform glass into a cutting-edge data storage solution.
As of fall 2023, Microsoft is set to unveil the workings of this visionary project, complete with a robotic system that retrieves data from glass sheets.
Here's how Project Silica works, its benefits, applications, and costs.
How Project Silica works
Glass's primary advantage as a data storage medium is its incredible durability.
Microsoft's Project Silica uses a femtosecond laser to etch data onto the glass, creating 3D units called "voxels."
A computer-controlled microscope interprets this encoded data, which is then stored in a library on glass sheets.
These sheets remain offline until accessed. Robots in the library move vertically and horizontally to locate and transport the data to the reader.
Once data is printed onto the glass and placed in the library, it becomes changeless, making it ideal for preserving content like books, music, and movies.
A single glass plate can store several terabytes of data, equivalent to approximately 3,500 movies, or around 1.75 million songs.
Cost of Project Silica storage
While Project Silica shows immense potential, its cost is a key consideration.
It may find use in preserving personal photos and videos for data-conscious users, but it's not ready for commercial adoption yet.
Microsoft outlines that the technology needs "3-4 more developmental stages."
Project Silica collaborates with the Microsoft Azure team to explore sustainable data storage approaches.
It also collaborates with Elire to create a Global Music Vault in Svalbard, Norway.
This vault can withstand extreme conditions and is highly durable.
While initial costs may be relatively high, Project Silica holds promise for the future.
As the technology matures and scales, costs are expected to decrease significantly.